IN commercial organizations, the amount of monthly remuneration paid to employees depends on financial capabilities of the company, its rating in the relevant sector of the economy, development prospects and management’s position on the issue of the amount of remuneration due to employees.
IN budget in organizations, the size cannot be set or adjusted by managers - this indicator is determined on regional and federal level, and is calculated on the basis of the Unified Tariff Schedule.
What is included?
The wage fund includes totality of all payments in cash and in kind, including social compensation, benefits provided by the enterprise for treatment, travel, recreation, and other purposes.
Main part of the savings - which is divided into direct and. The state establishes minimum indicator(), below which the organization and the entrepreneur do not have the right to make accruals, provided that the employee worked for full time.
Direct salary is accrued, depending on working conditions, in the form of a fixed salary, calculation for time worked () or for the volume of work performed (). In practice, more complex ones are also used, mixed forms remuneration (for example, piecework-bonus, piecework-progressive, piecework, etc.).
Additional the amount of accruals is a system of allowances and incentives determined by legislative provisions, as well as annual payments, additional payments for harmfulness, work at night and on weekends, expenses, and other payments related to the work process and provided for by the Labor Code.
We talked in detail about what is included in the payroll and wages.
Difference between payroll and labor force training
General salary fund consists of the main and additional ones. Thus it represents amount WTF (wage fund) and FMP (material incentive fund). FOT = ERT + FMP.
The Tax Code defines the amounts included in the Payroll Fund, for which the enterprise is obliged to accrue contributions to funds, and subject to income (). IN production cost includes direct and additional salaries, and the amounts of mandatory deductions determined by calculation.
In the same time, not all components the wage fund will be included in the cost price (in particular, dividends, interest accrued on shares, and incentives from distributed profits are not included). Incorrect distribution of expenses according to the articles leads to an unjustified reduction in income tax, as well as to errors in, which threatens the company with fines.
How are taxes calculated?
 The wage fund is the basis for calculating accruals in off-budget funds.
The wage fund is the basis for calculating accruals in off-budget funds.
According to current legislation, a business entity obligated to accrue and pay on time, determined by law, the following contributions:
- in (Pension Insurance Fund);
- V FSS(Social Insurance Fund);
- V Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund(Health Insurance Fund).
In its turn, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund, are divided into two groups: deductions for incidents, and deductions associated with injuries and occupational diseases. All transferred contributions are calculated on accrued payroll of the enterprise(and fund), and are included in the cost of products (services).
Today the tariff in the Pension Fund of Russia is 22% , in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund – 5,1% , in the FSS- 2,9% . Social contributions for injuries– an indicator established for each enterprise individually, taking into account the type of activity.
The legislation provides regulation of the amount of payments in the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. If more than 711 thousand rubles, then the amount exceeding this figure will be taxed at the rate 10% . The FSS provides zero contributions in excess of wages accrued in the amount of 670 thousand rubles.
Contributions are paid monthly, simultaneously with the payment. The law provides for the payment of remuneration to employees twice a month, on the days established by the enterprise (advance and settlement).
Reports to the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are submitted quarterly, on a cumulative basis. If payment deadlines or delivery deadlines are violated, administrative and financial penalties are imposed on the enterprise.
Let's consider example:
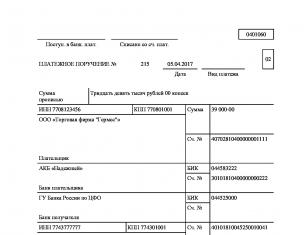
Payroll fund Panorama LLC amounted to 215 thousand rubles in April 2015. Costs for wages will be:

All mandatory deductions are calculated by economists when forming the wage fund, and are included in financial plan enterprises.
Personal income tax (NDFL)
This type of accrual reduces the amount of the employee's salary. Today the rate for a citizen of the Russian Federation is 13% , for (an employee who has citizenship of another country) – 30% . If an employee who is a resident is credited with 50 thousand rubles, then he will receive 43,500 rubles (50,000 - 6,500 = 43,500).
List of conditions for tax exemption or a reduction in the rate is established (in particular, deductions are reduced if there are minor children dependent on the parents, but the law is applicable only to one of the spouses).
Where are expenses recorded?
What is included in the wage fund in labor statistics? Payroll expenses taken into account, as already mentioned, when calculating contributions to funds, and when calculating taxes (single tax, income tax). This indicator is reflected in statistical, accounting and tax all business entities.
Employee income included in the payroll is the basis for calculating pension benefits. The amount of the wage fund and related charges are recorded in the relevant accounting documents, and actual payments for employees - in advance and payroll statements, expense orders.
Control
 Enterprise managers and owners must clearly understand fund formation mechanism, an accumulating fund for the payment of remuneration for labor, and mandatory contributions to the payroll.
Enterprise managers and owners must clearly understand fund formation mechanism, an accumulating fund for the payment of remuneration for labor, and mandatory contributions to the payroll.
Every change in payroll must be justified, and supported by relevant internal ones (protocols, orders, statements, calculations, etc.).
Correctly and timely completed salary documents are reliable legal protection business entity from fines and administrative penalties, since during tax audits close attention is paid correct formation of payroll and reflection of accruals in business transactions.
Regulations governing the procedure for calculating wages are often are changed and adjusted Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor legislation and make timely changes to the software.
The employee does not receive the full salary. Part of it is used to make contributions to funds and pay taxes. The entire list of payments is fixed in the current legislation.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
An employer cannot violate the rules and overcharge deductions from wages. To know exactly for what purposes the written-off funds are used and what is the maximum amount, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the latest information on the topic.
General information
Before you figure out which funds deductions from salary go to, it’s worth finding out what payments in favor of an employee are from a legal point of view.
Wages are the remuneration that an employer provides to an employee for carrying out work activities.
It can be issued in kind. However, in most cases, the organization provides the employee with a cash payment.
Salary may include:
- salary;
- incentive payments;
- other transfers specified in current legislation.
The employer is obliged to comply.
To find out all the nuances of the process and find out the amount of deductions, it is worth familiarizing yourself in detail with the features of each of the procedures performed.
Which funds go to?
The list of funds to which contributions must be made is clearly established by current legislation.
By withholding part of the employee’s salary, the employer is obliged to send the funds received to make payments to:
- MHIF.
Deductions are necessary so that government bodies can ensure the implementation of the citizen's constitutional rights to health care, pensions, social insurance and medical care.
Pension
According to the rules, the employer is obliged to send 22% of the employee’s total accrued wages to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
This is a big financial burden. However, thanks to the deduction, the employee will be able to count on a decent pension in the future.
Statistics show that a number of organizations are seeking to reduce the official amount of wages in order not to make contributions to various funds. Such companies can promise the employee a significant increase in actual payments. However, experts advise not to cooperate with such organizations.
Such behavior will significantly reduce the size of your pension in the future.
To the tax office
It is paid from the employee's salary. It is the main type of payment and is collected from the salary of each specialist.
Tax is calculated at the time of accrual of income. Payment occurs when a person receives a salary.
The amount of personal income tax withholding is 13% of earnings. According to, an employee can take advantage of tax deductions. They can be standard or social.
The first type of deduction is provided if the employee has a child. For the first offspring, 1,400 rubles are credited, and for subsequent babies or children with disabilities - 3,000 rubles.
This means that the size of the tax base from which contributions to the state are levied can be reduced by this amount.
Other
In addition to the main deductions, money is collected from wages and sent to the Social Insurance Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
5.1% of salary is transferred to the compulsory health insurance fund.
There is a limit on the amount. If it is achieved, the rate will be reduced to 10%. The amount of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund is 2.9%. The amount is sent to the payroll.
Some companies provide additional payments. So. A number of organizations ask workers to contribute to health and accident insurance.
The amount of deductions is determined by the organization. The payment amount varies from 0.2 to 8.5%.
What percentage?
The amount of payroll deductions can vary significantly depending on where the funds are sent.
Today, the following deductions must be made from the amount provided as wages:
- 22% towards the calculation of a future pension;
- 13% towards payment of personal income tax;
- 5.1% to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund;
- 2.9% to the Social Insurance Fund;
- from 0.2 to 8.5% for insurance against accidents that may occur at work (the exact amount depends on the risk class, which includes the profession and position of the employee).
Calculation procedure
Not all contributions are collected from the employee. Part of this is paid by the employer.
According to the rules, only 13% can be withheld from an employee's salary, levied as income tax. The remaining amount is taken from the wage fund. The employer must pledge it in advance.
Let's say an employee receives 10,000 rubles. In addition to this amount, the employer is required to pay a minimum of RUB 3,200. to funds and for the benefit of the state.
This amount consists of the following deductions:
- 2200 rub. to the Pension Fund of Russia;
- 310 rub. in the FSS;
- 510 rub. to the MHIF.
For this reason, the employer will have to invest not 10,000 rubles in the payroll, but 13,200 rubles. For the company, this figure will be the employee’s income.
Based on the above, in 2019 the employer is obliged to contribute at least an additional 30% to the payroll for making contributions to non-budgetary government organizations.
Some countries have a different payment method. The company provides the employee with the entire amount earned by him for a specified period, as well as a receipt with payments recorded in it that are to be made to various funds. The citizen pays taxes and current contributions on his own.
The taxation system is a complex system of economic relations and obligations between a subject and an object. This is a set of taxes and fees established legally in a particular state.
In the Russian Federation, the concept of payroll is an abbreviation for the wage fund. Why are these taxes paid, and what is the current procedure for their registration? This question worries every taxpayer.
Responsibility for tax evasion in the Russian Federation
Evasion is now considered a serious offence. First of all, contributions to the Payroll Fund are made so that wages, bonuses and rewards are calculated. Taxes are paid to this fund by employees of all enterprises - both government agencies and private firms.
The structure and size of the wage fund is an individual indicator for each enterprise, since these parameters directly depend on the number of officially employed workers. The average salary of citizens is also taken into account.
Categories of the wage fund
The following types exist:
- Payment for time worked by the employee.
- Payments for unworked time due to employee sick leave or vacation.
- Incentive payments (most often this is a one-time payment).
- Regular payments, if work duties require the employee to use a regular car, or travel allowances.
The tax contribution directly depends on the official payroll amount. Using the accounting program "1C ZUP", the chief accountant of the enterprise calculates tax deductions to the following mandatory funds:
- to the Pension Insurance Fund;
- to the Social Insurance Fund;
- to the Health Insurance Fund.
In 2019, on the territory of the Russian Federation, the amount of contributions to the payroll remained unchanged - this is a 30% rate, it will be maintained until 2019 inclusive. The payment deadline depends on the type of activity. Currently, the contribution rates for different funds are as follows:
- contributions for the Pension Insurance Fund – 22%;
- for the Social Insurance Fund – 2.9%;
- for contributions to the Health Insurance Fund - 5.1%.
For a more detailed understanding of the deduction process, it is worth giving an example. The wage fund of JSC Galaktika amounted to 311 thousand rubles in October 2019. Salary costs will be:
- for pension insurance – 47,300 rubles;
- contributions to the Medical Insurance Fund - 10,965 rubles;
- contribution for the Social Insurance Fund – 6,235.
This rate may increase if the facility has an increased potential for injury. Calculation under the simplified tax system occurs according to the same algorithm.
Why is this tax needed?
Taxes to the Payroll Fund are an important component of decent earnings and material compensation for workers in a wide variety of enterprises and fields of activity. Any change in the amount of remuneration must be immediately reflected in the enterprise’s document flow and be justified. A deduction in the amount established by the state, when the fixed rate is 30%, allows you to insure the employee in the necessary funds. An ordinary employee of an enterprise does not personally calculate or prepare a tax contribution; in an enterprise this function is performed by the accounting department, dealing with all postings. Accountants monitor the accuracy and, most importantly, the timeliness of deductions.
What payroll taxes does the state require from Russian individual entrepreneurs and legal entities? The wage fund consists not only of wages, but also of all transfers by the employer in favor of employees. Most of these charges are taxable. In addition to taxes, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities are required to make monthly payments of certain other mandatory payments. We describe which ones exactly below.
General list of taxes and mandatory payments from the payroll
In accordance with Russian legislation, individual entrepreneurs, all enterprises and institutions that hire employees, act as their tax agents and make monthly deductions from the payroll fund.
The employees themselves, that is, individuals, are excluded from the process of transferring taxes. They can only find out about the payment of mandatory payments from a salary “receipt” or a certificate in form 2-NDFL.
This procedure was adopted for the convenience of the federal tax service. It is easier for its employees to control organizations than to deal with each taxpayer separately.
Charges to the wage fund appear monthly.
Charges to the wage fund appear monthly. The task of each employer is to pay them within the period prescribed by law and in full. This list includes:
- Taxes on personal income - on employee wages, sick leave and vacation pay, bonuses and other payments that are transferred to employees based on the results of their professional activities.
- Mandatory transfers to specialized funds - pension, as well as social and medical insurance.
Characteristics of taxes and mandatory payments from the payroll
Next, we will look in detail at what wage accruals are required by law from employers in 2018, during what time periods, and in what volume. Also, all categories of mandatory payments and taxes will be presented below in the form of a convenient table.
Timely payment of personal income tax for all employees is an important part of payroll payments
The main payroll tax is personal income tax., personal income tax. The amount of this tax paid by residents of the Russian Federation - and this includes the majority of employees - is 13% of the total accrual amount.
If the organization’s staff includes a foreign citizen, that is, a tax resident of another state, 30% of the accrual amount is required to be paid to the Russian budget. Such situations occur much less frequently in practice, but they are still worth remembering.
Tax payment is made on the same day as the transfer (issue) of money to the employee. Most often, personal income tax is paid on wages, as well as vacation pay, sick leave and bonuses. Please note that it is necessary to pay personal income tax on wages only once a month; payment of this tax on the so-called “advance” is not provided.
Mandatory payments from the payroll to various funds
The law also obliges employers to make monthly several types of mandatory payments for employees in favor of various insurance funds - social and medical. It is also the responsibility of entrepreneurs and organizations to pay pension contributions for all their employees.
Currently, the following rates are provided for these categories of payments (of the total payment amount)::
- health insurance - 5.1%;
- social insurance - 2.9% (can be increased in hazardous and hazardous industries);
- pension contributions - 22%.
note that individual entrepreneurs are not required to pay social insurance contributions, this category applies only to legal entities. An exception is the situation when an entrepreneur wants to transfer funds to social insurance voluntarily.

The law obliges employers to make monthly several types of mandatory payments for employees in favor of various insurance funds.
Balance sheet data - where is the payroll and where is the full salary
The wage fund in the balance sheet is recorded on credit 70, in debit lines 91, 26, 25, 20 and 08. Do not confuse payroll with payroll- the latter contains exclusively transfers to employees for work activities minus all other payments. The wage fund in the balance sheet is recorded in K70 D20.
Table - all payments and transfers are clear
In order not to get confused in the list of mandatory payments assessed by the state on the wage fund of individual entrepreneurs and legal entities, use the simple and convenient table below.
| Tax, contribution or payment | Rate (based on the amount charged) | Some nuances |
| Personal income tax | 13% or 30% | Tax residents of Russia pay personal income tax in the amount of 13%, citizens of foreign countries - 30%. |
| Pension contributions | 22% | Pension contributions are also paid by certain categories of foreign citizens, this is due to the status of their presence on the territory of the Russian Federation. |
| Social insurance contributions | 2,9% |
This is a standard rate, which can be increased depending on the harmfulness and danger of production. Paid only by legal entities, individual entrepreneurs - only at will. |
| Health insurance | 5,1% | — |

Russian legislation provides for penalties for non-payment of any taxes and mandatory payments.
Example of calculations and transfers - calculation of payroll and all mandatory payments
Let's look at how the volume of taxes and mandatory payments from the payroll fund is calculated in 2018 using the example of the fictitious organization LLC "Flowers". Let’s assume that the organization employs 18 employees, 16 of whom are tax residents of Russia (that is, they pay 13% personal income tax), and the other 2 are non-residents (that is, 30% personal income tax for them).
The salary of 5 employees is 15,000 rubles (including two foreign citizens), 5 others - 18,000 rubles, 3 - 25,000 rubles, 4 - 30,000 rubles and 1 - 40,000 rubles. No other accruals other than employee wages were made this month. First, we calculate the size of the wage fund for this month:
(5 * 15,000) + (5 * 18,000) + (3 * 25,000) + (4* 30,000) + 40,000 = 400,000 rubles.
At the same time, the total salary of tax residents is 370,000 rubles, and non-residents - 30,000 rubles. Now let’s calculate what and in what amount the employer will pay to the budget and insurance funds:
- Personal income tax of tax residents. 370,000 * 13% = 48,100 rubles.
- Personal income tax of non-residents. 30,000 * 30% = 9,000 rubles.
- Pension contributions. 400,000 * 22% = 88,000 rubles.
- Health insurance premiums. 400,000 * 5.1% = 20,400 rubles.
- Social insurance contributions. 400,000 * 2.9% = 11,600 rubles.
Thus, the total value of all mandatory payments to the budget and insurance premiums for an organization whose monthly payroll amounted to 400,000 rubles will be 177,100 rubles. That is, the cost of paying employees and accompanying accruals will be equal to 577,100 rubles.
Responsibility for non-payment of taxes from the payroll
Russian legislation provides for penalties for non-payment of any taxes and mandatory payments, as well as late transfer or failure to pay on time. For overdue insurance premiums, you will have to add 20% to 40% of the unpaid value to the payment amount. Failure to pay taxes on time will result in an administrative fine. Its size, as a rule, is from 2 to 5 thousand rubles.
Conclusion
In the Russian Federation, employers perform the duties of tax agents for hired employees, therefore, from the entire wage fund. Thus, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are required to timely pay taxes to the budget and insurance transfers to specialized funds. For failure to fulfill these obligations, regulatory authorities have the right to impose penalties on the employer.
Each employee receives a salary from which certain funds are deducted. Let's consider what amounts and when can be withheld from wages in accordance with the current legislation of Russia in 2019.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
When carrying out an audit, categories of employees, types of accruals and features of their payments are determined. In order for the audit to go smoothly, it is worth understanding some of the rules for deductions from employee earnings.
Basic moments
What is meant by the concept of “wages” and when should they be paid?
Concepts
Wages are monetary remuneration (sometimes in kind) paid by an employer to its employee for work performed.
The salary may include salary, incentive payments and other transfers prescribed in legislative documents.
Terms of salary payment
Just add a clause about the period of work after training in. Usually the period of work after graduation is set at 2-3 years.
Let us repeat that reimbursement of training costs is necessary if the contract is terminated for an unjustifiable reason. But in the legislation there is no division into respectful or disrespectful.
Therefore, such moments should be provided for in employment contracts. The employer may withhold the following funds:
- the amount spent on the study itself;
- amounts spent on travel to the educational institution;
- stipend that was paid by the company, etc.
For a work book
Let's consider the rules of paragraph 47 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, preparing a form for such a document and providing security or employer in accordance with the regulations.
If an employee is issued a work book or an insert in it, the employer withholds the amount spent on the purchase of such documents.

Exceptions are made in cases provided for in paragraphs 34, 48:
Payment for a new sample work book must be made by the employee to whom it is issued. And the date of issue is the day of termination of the employment contract.
And at the same time, it is worth remembering that the amount should not be set by employers - it should be equal to the funds that were spent on the purchase.
Seizure procedure
When considering the set of accruals, it is worth stipulating what deductions are not made from funds paid:
- In order to compensate for damage caused to health, compensation for harm caused to a person upon the death of the breadwinner.
- A person who was injured (wounded, shell-shocked) while performing work duties, and his relatives if such a person dies.
- At the birth of a baby, a parent with many children, a single parent, for the maintenance of a child under the age of majority (if his parents are wanted), for alimony obligations, for an elderly person or a disabled person to care for him, for additional food.
- For performing work under harmful conditions or in an extreme situation, as well as to a person who has suffered from exposure to radiation at a nuclear power plant or in other situations provided for by legislative acts.
- Company at the birth of a baby, death of a relative, marriage ().


Order to deduct from wages
When a deduction is made by the management of the enterprise, an order of the following form must be issued:




Features for a foreigner
The rules for withholding will be determined depending on where such person works (domestic or foreign) and whether he is a resident.
If the foreign employee is a resident, income tax is charged at 13%. Non-residents are charged 30%.
The exception is an employee who is considered a highly qualified specialist (13% is charged). It is worth considering that agreements are drawn up between the Russian Federation and some countries.
If such documents contain relevant clauses, a foreign worker may not pay taxes in Russia.
The decision will be made by tax authorities in accordance with. Profit received outside the state is taxed if the foreigner is considered a resident of the Russian Federation ( – ).
The right to use the standard deduction appears in cases where a foreigner becomes a resident ().
Insurance contributions to the Pension Fund from the profit of a foreigner are withheld if the person resides in the territory of the Russian Federation on a temporary or permanent basis.
In the first case, contributions are withheld:
- if a permanent employment contract has been concluded;
- if the employment contracts are valid for at least six months in the billing period, otherwise the foreign citizen will not be considered insured by the Pension Fund of Russia;
- if several employment contracts have been concluded for a certain period, the total duration of which exceeds six months;
- if a person works in accordance with a fixed-term employment contract, which was concluded in the billing period for a period of up to six months, and after that it was extended (and the period of 6 months was exceeded).
Pension contributions, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund are paid from the income of all working foreigners, except those considered to be temporarily staying in the country. The accrual rules should be applied the same as in general cases.
Maximum payout amount (limit)
In accordance with the general rules, the amount of deduction from earnings should not exceed 20% of the funds accrued to the citizen.
A different procedure should be followed if there are writs of execution.
Thus, the Law of July 21, 1997 No. 119-FZ states that when fulfilling the provisions of the writ of execution, more than 50% of the amounts earned should not be withheld until full payment.
When fulfilling several executive documents, the employee must receive at least half of the salary.
Such restrictions do not apply if the person:
- performs correctional work;
- pays alimony for the maintenance of a minor child;
- compensates for damage caused to health, etc.
In such situations, retentions can be up to 70%.
Deductions from the minimum wage
The minimum wage is the same income as any other wage. This means that it can be the tax base from which taxes are levied.
It happens that employees consider the write-off of certain amounts to be unlawful. For example, is it legal to withhold a large part of the minimum wage to pay off debt on housing?
If the citizen gave such consent when drawing up the contract, then the employer has the right to withhold funds.
Questions that arise
Let's look at some of the nuances when deducting funds from earnings.
How to reduce (minimize) taxes on salary?
Let's analyze existing ways to reduce the amount of tax payments:
| When paying income tax for an individual, you must use the right to deductions | Which are presented at the request of the employee. When concluding a contract, find out what benefits are provided to staff and ask for the relevant documents |
| Regarding social contributions | It is necessary to fill out all sheets of temporary disability. Such actions will help reduce the tax payment. Don’t be lazy to contact your doctor with a request for an official document |
| Concerning contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases | Try reducing your tariff. At the initiative of the employer, an application can be submitted to the Social Insurance Fund with a request to reduce tariffs. This opportunity is presented to companies that pay everything on time and have no complaints during an on-site inspection. The probability is not high, but in some cases, consent can still be obtained |
| Streamline the transfer of bonus amounts and dividend payments | Organize uniform leave arrangements for employees and engage in inventory planning |
Regarding the childlessness tax
In the USSR, workers who did not have children paid the appropriate tax. It amounted to 6% of the salary. The government stopped withholding such amounts in early 1992.
But in 2013, a proposal was put forward to resume payment of the tax for childlessness, which still has no expression in legislative documentation.
At the moment, a person who has a child may not have to pay personal income tax on 1.4 thousand rubles. This is 182 rubles. tax per month.
If an employee has several children, then a deduction is possible from the amount of 3 thousand for the second and each subsequent child, which is 390 rubles. Many people call this deduction a childlessness tax.
Citizens who do not have children pay 2 thousand rubles more in taxes than their employees who have a child.
If one parent has taken advantage of the child deduction, then his spouse can no longer take advantage of this right. That is, the family receives tax exemption.
How much interest can bailiffs retain?
The Law “On Enforcement Proceedings” discusses how much bailiffs can deduct from wages.
When determining the size, it is worth considering what amount will remain after all the necessary funds have been withheld. It is a known fact that the amount of deductions cannot exceed half of a person’s earnings.
The exact amount of deductions will depend on the number of writs of execution and the amount of the salary itself.
Such a restriction will not apply if it is necessary to pay alimony or the amount of compensation for the loss of a breadwinner. Then up to 70% can be retained.
Funds are withheld under a writ of execution without the consent of the citizen or the issuance of special orders from management. The list of executive documentation is in Art. 7 of the normative act of July 21, 1997 No. 119-FZ.
If you have a child, is your income tax reduced?
Those persons who have children can reduce the amount of income tax by 1.4 (for the first-born) or 3 thousand rubles (for the second child). Guardians can also use such deductions.
The rules for reducing personal income tax do not apply to the earnings of persons who are trustees and adoptive parents.
Parents of minor children have the right to use the benefit if their earnings do not exceed 280 thousand.
It is also possible to take advantage of the deduction for employees whose child is a student or graduate student, if he is under 24 years of age.
Where does income tax go?
Income tax is considered a federal payment, the amount of which is distributed between the local and regional budgets.
But there is no rule that personal income tax must be credited to the appropriate budget:
Can they be deducted for workwear upon dismissal?
If the employee has handed over the workwear, the company does not have the right to withhold its value. Otherwise, an individual may go to court within 3 months after dismissal.
Figure out what funds can be withheld from earnings, and then problematic situations will not arise during the work process.
Attention!
- Due to frequent changes in legislation, information sometimes becomes outdated faster than we can update it on the website.
- All cases are very individual and depend on many factors. Basic information does not guarantee a solution to your specific problems.